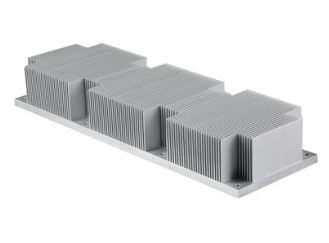
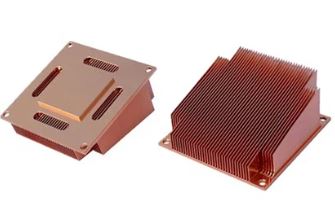
Skived
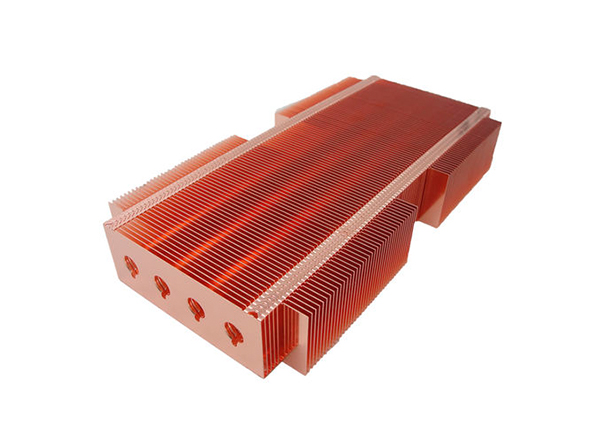
A skived air heatsink is a type of heat dissipation device commonly used to cool electronic components such as CPUs, GPUs, or industrial devices. Skived (or "skiving") technology involves a machining process in which very thin fins are cut directly from a solid block of metal (usually copper or aluminum) using a cutting tool. The fins are then lifted without being separated from the base block, creating a single body with high thermal conductivity.
Main features
High thermal efficiency, thanks to the strong bond between base and fins (no welding or gluing)
Higher fin density, which increases the heat exchange surface with the air.
Excellent weight-to-performance ratio, especially in applications where compact dimensions are important.
These heatsinks are often used in contexts where effective cooling with passive or low-noise solutions is required.